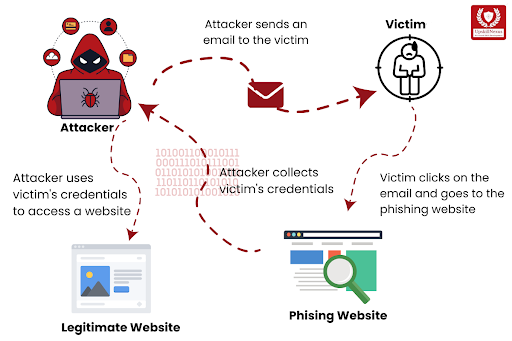
Hey CyberFolks, Welcome back to the blog series.
If basic phishing scams are the pickpockets of the cyber world, advanced phishing techniques are the con artists in tailored suits—” ‘slick’, ‘calculated’, and ‘devastatingly effective’. These attacks do not simply target your bank information or passwords; they also target entire corporations, governments, and even nations, frequently causing chaos in their wake.
Here is the good news: Like attackers develop and enhance their tactics, so can we. Understanding the complexities of advanced phishing and arming ourselves with cutting-edge tools and methods will allow us to defeat even the most sophisticated schemes. This detailed instruction is the next step towards becoming a cyberdefender. Let us break down sophisticated phishing strategies, look at real-world examples, and equip you with strong countermeasures to stay ahead.
What Is Advanced Phishing?
Unlike Classic Phishing Scams, which rely on the Bulk Circulation of Bogus Emails, advanced Phishing uses highly customized strategies to target specific persons and organizations. These attacks frequently bypass classic security measures by utilizing social engineering techniques, complex malware and cutting-edge technologies.
Key differences include:
- Personalization: Messages are customized to appear real.
- Technology exploitation: the use of artificial intelligence, deepfakes and advanced spoofing.
- High-stakes: targets frequently include C-level executives, finance departments, and IT administrators.
Understanding Advanced Phishing Techniques
1. Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) Phishing
Attackers intercept communications between two parties, manipulating data in real time. Public Wi-Fi hotspots are typical targets for such attacks, as people unintentionally connect to malicious networks.
Assume a passenger connects to free airport Wi-Fi, unaware that their login information is being captured and forwarded to attackers.

2. Business Email Compromise (BEC):
BEC is a productive phishing technique in which attackers mimic high-ranking authorities or trusted partners to trick employees into transferring payments or disclosing sensitive information.
In December 2024, the Delhi Police’s Intelligence Fusion and Strategic Operations (IFSO) uncovered a BEC scam where fraudsters impersonated executives to steal over Rs 7 crore from Delhi firms..

3. Deep Fake Phishing
Attackers use artificial intelligence to create realistic voice or video mimicry that mislead victims to act on bogus requests.
Real-world Example: In 2019, a deepfake voice imitating a CEO authorized a $240,000 transfer, deceiving a multinational corporation’s finance department.
4. OAuth Exploitation
Attackers fool users into giving rights to malicious apps by tampering with OAuth protocols. Attackers can take control of cloud storage, email accounts, and more if access is authorized.
5. Watering Hole Attacks
Attackers compromise websites that their targets visit regularly. These sites then redirect victims to phishing pages or malware downloads.
For example, sensitive information was stolen when a compromised government website targeted defence contractor personnel.

6. QR Code Phishing
Phishing with QR codes is becoming more common. Attackers lure naive people to phishing websites by embedding malicious codes into emails, posters and ads.
There are many other types of phishing like Email Phishing, Vishing, Smishing, CEO Fraud(Business Email Compromise- BEC), Social Media Phishing, Search Engine Phishing, Pop-Up Phishing, Angler Phishing, Watering Hole Phishing, Evil Twin Phishing, Malvertising etc.
Advanced Detection Techniques
Vigilance and specific technologies are necessary for the effective detection of sophisticated phishing assaults.
1. Analysis of Email Headers
- DMARC, DKIM, and SPF Exams: Verify if the sender is legitimate.
- Mismatched Fields: Identify discrepancies between “From” and “Reply-To” addresses.
- Examine email headers for irregularities using programs such as MXToolbox.
2. URL Inspection
- To confirm a link’s actual destination, hover over it.
- Look for instances of homoglyph assaults, such as “g00gle.com” being used in place of “google.com”
- For in-depth checks, use scanners such as VirusTotal or URLScan.io.

3. SSL/TLS Certificate Validation
- Verify that domain names match and that certificates are authentic.
- Avoid websites with expired or self-signed certificates.
4. Sandbox Analysis of Attachments
- Use sandboxing tools such as Cuckoo Sandbox to examine email attachments for possibly harmful activity.
- Verify file hashes by cross-referencing them with threat intelligence databases such as VirusTotal.
5. Behavioral Analytics
- Use machine learning-based tools to spot unusual user activity, like login attempts from unfamiliar devices or places.
Real-World Examples of Advanced Phishing
Operation Aurora
A cunning campaign compromised authentic websites that employees of Fortune 100 businesses frequented to target them. Users were sent to fraudulent websites that installed malware and collected login details.
COVID-19 Phishing Scams
Attackers took advantage of people’s Fear and Confusion during the epidemic by pretending to be medical institutions like the CDC or WHO to transmit malware or steal login credentials.
Spear Phishing Against Political Entities
Attackers have affected elections and policymaking by obtaining sensitive political information through spear-phishing emails.

How to Defend Against Advanced Phishing
1. Deploy Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Even in cases where credentials are compromised, Unauthorized access can be avoided by implementing an additional layer of security. The most robust resistance is offered by hardware-based tokens, such as YubiKeys.
2. Invest in Secure Email Gateways (SEGs)
Modern SEGs use AI to filter out phishing emails, identifying threats based on content, metadata, and sender reputation.

3. Implement Zero-Trust Architecture (ZTA)
- Verify every device and user trying to connect to your network.
- Keep an eye on and assess trust levels at all times.
4. Regular Employee Training
- To test and train staff, conduct phishing simulations.
- For engaging training modules, utilize platforms such as Cofense or KnowBe4.
5. DNS Filtering
- Use DNS-based solutions, such as OpenDNS, to prevent access to known malicious domains.
6. Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)
- Use EDR tools to keep an eye on user devices and respond to any suspicious activity.
- SentinelOne and CrowdStrike Falcon are two examples.
7. Use Threat Intelligence
- Keep updated on phishing tactics, techniques, and indicators of compromise (IOCs) by utilizing global threat intelligence feeds.
Emerging Trends in Advanced Phishing
AI-Driven Phishing:
Cybercriminals are using AI more and more to create incredibly customized phishing emails that look real and bypass spam filters.
IoT Targeting
As the number of IoT devices increases, hackers take advantage of vulnerabilities in these devices to access larger networks.
Mobile Phishing
Phishing campaigns that use apps and SMS (smishing) to target mobile users are getting more common.
Social Media Phishing
On LinkedIn and other sites, phoney accounts trick users into installing malware or disclosing private information.
Advanced Tools to Combat Phishing
- PhishTank: An open-source tool for identifying and reporting phishing websites.
- Spamhaus: Blocks harmful domains to prevent spam and phishing.
- Splunk Phantom: Automates phishing attack detection and response.
- Gophish: A platform for simulating phishing attacks to evaluate staff awareness.
- IBM QRadar: Offers phishing detection and enhanced threat intelligence
Statistics Highlighting the Threat
- Global Impact: In 2023, 83% of all cyber incidents recorded by enterprises were caused by phishing.
- Financial Loss: Last year, phishing attempts caused damages totaling more than $5 billion.
- Time to Breach Detection: Phishing-related breaches go undetected for an average of 77 days.
Case Study: A Spear-Phishing Attack on a Financial Institution
The finance department of a financial institution was the target of a spear-phishing attack in 2022. The attackers asked for a $3 million urgent wire transfer while impersonating the CFO. The money had already been transferred between several accounts by the time the crime was discovered, making recovery practically impossible.
Lessons Learned:
- Always use secondary communication channels to confirm high-value transactions.
- Establish transaction thresholds that require two-way permission for transfers.
Summary: Staying Ahead of the Curve
Advanced phishing techniques pose a constant and dynamic risk. However, people and organizations are able to fight off these attacks by being aware of their processes, developing resources with strong defences, and cultivating a culture of cybersecurity awareness.
Our goal at UpskillNexus is to equip professionals with the most up-to-date information and resources possible to fight phishing and other online dangers. Keep yourself updated, remain alert, and Join us to create a safe digital future.
Looking to enhance your cybersecurity skills? Follow our blog series for expert insights and practical advice. Together, let’s make the digital world a safer place!