The Impact of Quantum Computing on Cryptography: What You Need to Know

A New Era of Cybersecurity Challenges
Technology is growing at an unprecedented pace and innovation has captured the imagination of researchers and businesses alike: quantum computing assures progress in fields like medicine, artificial intelligence and material science; it also poses a significant threat to the world of cryptography. At Upskill Nexus, we are dedicated to keeping you informed and prepared for the challenges of tomorrow. Here’s everything you need to know about the impact of quantum computing on cryptography.
What Is Quantum Computing?
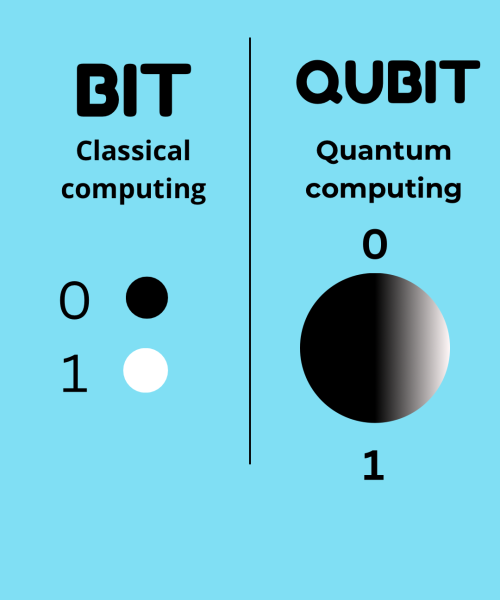
Before we dive into quantum computing, let us understand what quantum computing is. Quantum computing is a comprehensive field that influences peculiar principles of quantum mechanics to derive information in ways traditional computers fail to do. The fundamental difference between classical and quantum computing is the use of qubits by the latter in place of bits (a binary digit that represents a logical state with one of two possible values: 0 or 1), which gives it access to encode information in multiple states, simultaneously through quantum superposition. This allows and adds an advantage for quantum computers to do various calculations simultaneously, hence solving complex problems much faster than classical computers. In simpler terms, the rate at which quantum computers process information is much faster than traditional computers, which would take years to process that same information.
How Quantum Computing Threatens Cryptography
Digital security is the solid backbone of cybersecurity, for which cryptography acts as a foundation. Cryptography ensures that our personalised information is kept confidential, from personal data to financial transactions. The potential ways in which quantum computing threatens are:
1. Breaking Rivest-Shamir-Adleman (RSA) and Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC)
Encryption refers to the process of protecting information or data by using mathematical models to scramble it so that only the parties with the key to unscramble it can access it. RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) and ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography) are the two encryption methods widely used in cybersecurity. These rely on mathematical problems that are computationally hard to solve, meaning the difficulty of factoring large numbers or solving discrete logarithms. An example would be factoring large numbers, which involves breaking down a large number into its prime factors. Let us take a case: given a number like 323, it is relatively easy to check that 323 = 17 19, but for huge numbers with hundreds or thousands of digits, factoring becomes extremely difficult with current computational methods.
Similarly, discrete logarithms refer to solving equations of the form gx y (mod p) for x, where g, y and p are known. While it’s straightforward to compute y from g and x, reversing the process (finding x) is computationally hard for large values.
2. Impact on Symmetric Cryptography
The AES—Advanced Encryption Standard AES stands for Advanced Encryption Standard, a symmetric block cypher algorithm that encrypts data. It protects sensitive data, such as classified information, chat messages and legal documents. It is more prone to quantum attack, but Grover’s algorithm (Grover’s algorithm speeds up the solution to unstructured data searches, running the search in fewer steps than any classical algorithm can) could still reduce their security levels. This means key sizes may need to double to maintain the same level of security in a post-quantum world. This algorithm solves several problems. For example, it helps in finding patterns in data, breaking cryptographic keys and solving optimization problems. The power and usage of quantum computing will increase and simultaneously, Grover’s algorithm will become exponentially important.
3. Threat to Blockchain
Blockchain relies on cryptographic techniques for transaction security. Quantum computers could potentially compromise the cryptographic signatures used in blockchain, posing a risk to its integrity and trustworthiness.
Preparing for the Quantum Era
To mitigate the risks associated with quantum computing, researchers and organizations are developing post-quantum cryptography (PQC). These cryptographic methods emphasize the security of both classical and quantum computing.
Key initiatives include:
1. NIST’s Post-Quantum Cryptography Standardization
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is working to develop and standardize quantum-resistant algorithms. This initiative ensures that organizations can seamlessly transition to secure cryptographic methods.
2. Hybrid Cryptographic Systems
Many organizations are about to adopt hybrid systems that combine traditional and quantum-resistant algorithms. This approach will act as a transitional solution until quantum-resistant methods are widely adopted.
For secure communication, QKD is another masterpiece that uses quantum mechanics. It ensures that any interception of the key is detectable, making eavesdropping virtually impossible.
The Role of Upskilling in Cybersecurity
At Upskill Nexus, we agree that staying ahead of emerging threats requires continuous learning. Our cybersecurity training programs are designed to equip you with the knowledge and skills needed to navigate the challenges of the quantum era. Here’s how we can help:
- Foundations of Quantum Computing: Achieve a basic understanding of quantum principles and their implications for cybersecurity.
- Post-Quantum Cryptography: Learn about quantum-resistant algorithms and their applications.
- Practical Workshops: Participate in hands-on projects to implement secure systems in a post-quantum world.
- Certification: Earn credentials that demonstrate your expertise in quantum-era cybersecurity.
Who Should Be Concerned About Quantum Computing?
Quantum computing’s impact on cryptography affects a wide range of organizations and institutions, including:
- Financial Institutions: Secure sensitive financial data and transactions.
- Healthcare Providers: Protect patient records and research data.
- Government Agencies: Safeguard classified information.
- Technology Companies: Future-proof systems against quantum threats.
Whether you’re a cybersecurity professional, IT specialist or business leader, understanding the implications of quantum computing is critical to staying ahead in a rapidly changing world.
The Upskill Nexus Advantage
By choosing Upskill Nexus, you’re investing in a future-proof skill set. Our expert-led training programs are designed to:
- Keep you informed about emerging technologies.
- Equip you with actionable strategies to mitigate risks.
- Empower you to take proactive steps in securing digital assets
Let’s Start Today!
The quantum era is on the horizon, and the time to act is now. At Upskill Nexus, we’re here to guide you every step of the way. Take control of your future and become a leader in quantum-resistant cybersecurity.